A new backdoor for MacOS systems has been discovered in recent days by ESET researchers. The goal of the malware is to exfiltrate information from the victim system by exploiting cloud storage services.
The Backdoor, named by CloudMensis researchers, recovers information such as documents, email messages and attachments, files on removable devices, screenshots and the sequence of keys pressed by the user from the victim system.
CloudMensis is a serious threat to Mac (Apple) users, but its very limited distribution suggests it is a tool used in targeted offensive operations.
“We still don’t know how CloudMensis is initially deployed and who the targets are. The overall code quality and lack of obfuscation shows that the authors may not be very familiar with Mac development and are not that advanced. However, many resources have gone into making CloudMensis a powerful spying tool and threat to potential targets.” explains ESET researcher Marc-Etienne Léveillé, who analyzed CloudMensis.
CloudMensis – Steps of the infection
After launching into the victim system, CloudMensis performs Privilege Escalation tasks to execute code with maximum privileges by exploiting four different vulnerabilities and clearing traces from the Safari sandbox.
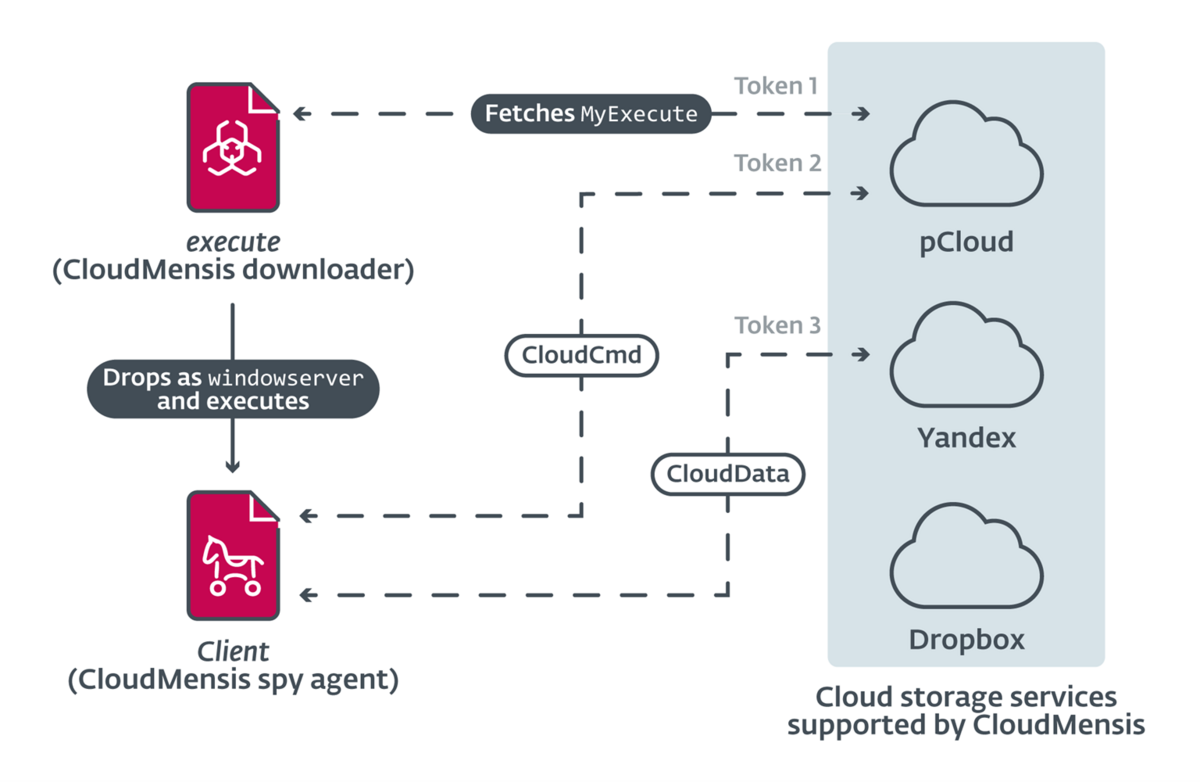
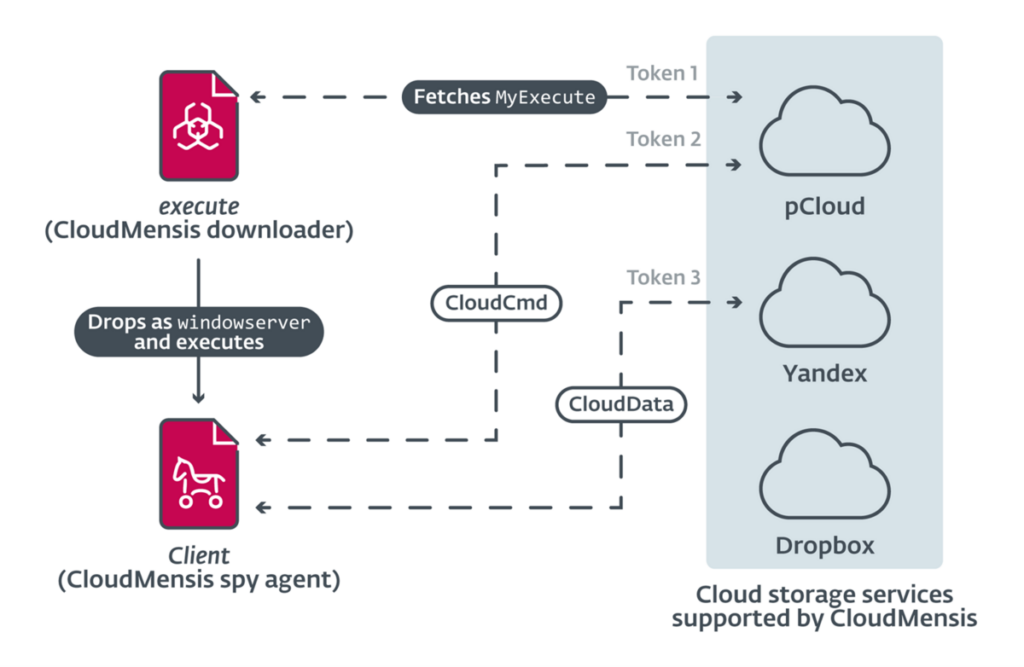
The first stage deals with the download from a cloud storage service of a second, more advanced stage necessary for collecting information from the compromised system. In total there are 39 commands for exfiltrating documents, screenshots, email attachments and other sensitive data.
The second stage exploits a vulnerability (CVE-2020-9934) to bypass the Transparency Consent, and Control (TCC) security framework, a framework that ensures that all apps obtain explicit user consent to access files in Documents, Downloads , Desktop, iCloud Drive, and network volumes.
What complicates CloudMensis Threat Detection activities through Network Security activities is the use of cloud storage services both for file exfiltration and for the exchange of commands (Command & Control, C2). The malware appears to support three different providers: pCloud, Yandex Disk and Dropbox.
The Malware began transmitting commands to command and control servers starting February 4, 2022.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
- Downloader (first stage)
- SHA256 273633eee4776aef40904124ed1722a0793e6567f3009cdb037ed0a9d79c1b0b
- Client (second stage)
- SHA256 317ce26cae14dc9a5e4d4667f00fee771b4543e91c944580bbb136e7fe339427
- Client (second stage)
- SHA256 b8a61adccefb13b7058e47edcd10a127c483403cf38f7ece126954e95e86f2bd